Overview
MotDet is a web based application which allow user to identify distribution characteristics of variants of consensus or query motifs within or or more submitted source sequences. Motif is a small strech of nucleotide sequence which are likely to have biological significance such as core promoter element, binding site for regulatory protein like activators, repressors or its association with structural motifs found in proteins.
MotDet provides three functions for motif detection:
1. Identification of significant covariants.
2. Identification of significant common variants.
3. Identification of the variants specific to the submitted source sequences.
To perform the aforementioned functions, software splits the sequences into small blocks of nucleotides. Each such blocks are then assessed for covariants and common variants.
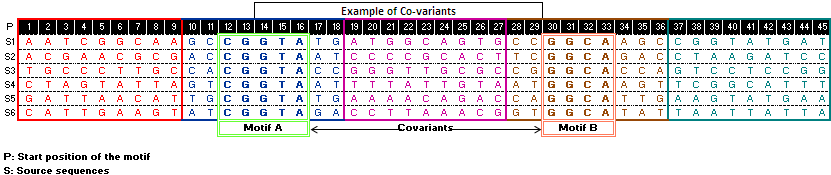
Example of co-variants
Example of common variants
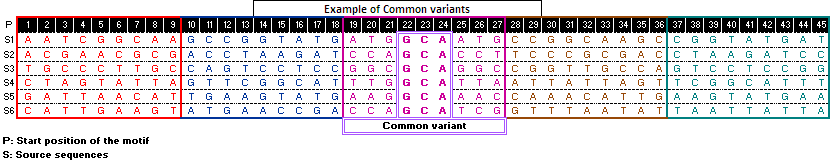
Such kind of analysis for set of co-regulated genes could lead one towards identification of conserved motifs. Thence give insight into co-expression and co-regulation of genes in same tissue and condition.
MotDet is developed in PERL/CGI deployed on Linux server located at Institute of Bioinformatics and Biotechnology (IBAB), Bengalooru, India. Application can be executed on web browsers such Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Safari. However browser should be JavaScript compatible.
Steps to follow
There are three basic steps to analyze the given query sequences for motifs using MotDet. Following are those steps:
1. Input the motifs.
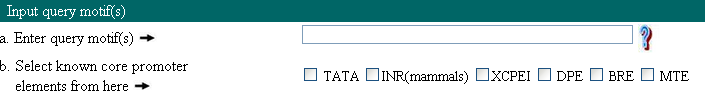
User can enter the custom motifs of length ranging from 5-20. These motifs can be specific pattern or the consensus sequences. Consensus motifs should adher IUPAC format.
IUPAC Format
|
Symbol
|
Represents what?
|
Why this symbol?
|
|
G
|
G
|
Guanine
|
|
A
|
A
|
Adenine
|
|
T
|
T
|
Thymine
|
|
C
|
C
|
Cytosine
|
|
R
|
G or R
|
puRine
|
|
Y
|
T or C
|
pYrimidine
|
|
M
|
A or C
|
aMino
|
|
K
|
G or T
|
Keto
|
|
S
|
G or C
|
Strong interaction (3H bonds)
|
|
W
|
A or T
|
Weak interaction (2H bonds)
|
|
H
|
A or C or T
|
not-G, H follows G in the alphabet
|
|
B
|
G or T or C
|
not-A, B follows A
|
|
V
|
G or C or A
|
not-T(not U as it stands for uracile), V
follows U
|
|
D
|
G or A or T
|
not-C, D follows C
|
|
N
|
A or G or C or T
|
aNy
|
User can also select motifs from the pre defined list. This list is produced after extensive literature search for few mammalian species.
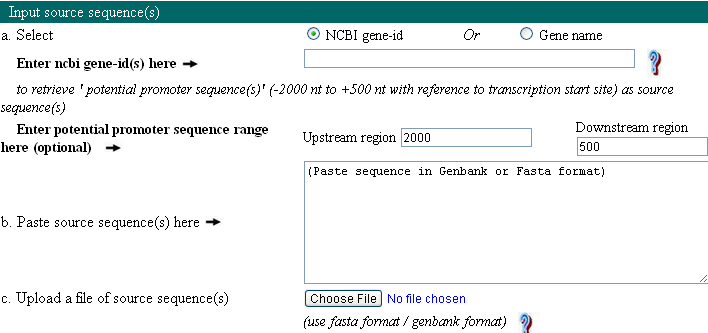
2. Input query sequences.
Query sequence should be nucleotide sequences which will be analyzed for user defined motifs. There are four modes to provide this input: Gene ID, Gene name, upload the sequence, and paste the sequence. Gene ID and Gene name with specified organism will extract potential promoter sequence from either NCBI or local database depending upon sequence information availability. User can also upload or paste the sequence in FASTA or Genbank format. Click FASTA or Genbank for example. Software works well with query sequence input upto 1 MB.
3. Input other mandatory inputs
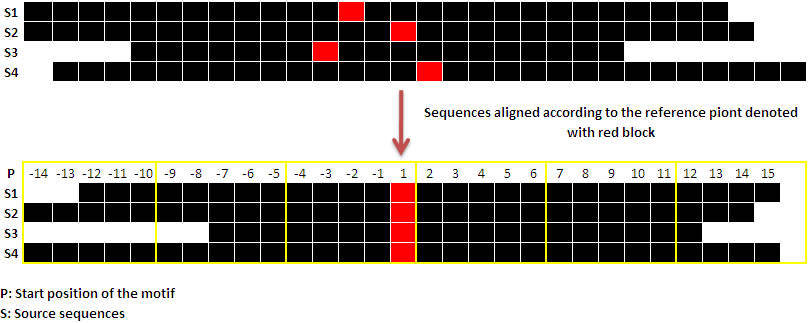
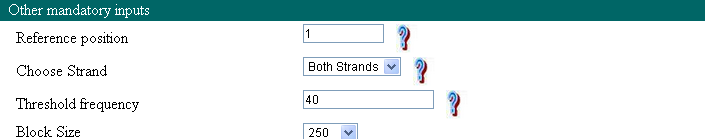
Reference position: As explained in Overview, submitted query sequences are divided into blocks of nucleotides. Before dividing the sequences, they are aligned to each other with respect to some position for e.g. reference point of the gene. Aligning sequences in this manner would help denoting sequencing upstream and downstream uniformly, and hence would aid in block wise analysis of the sequences for motifs. Therefore, reference point plays an important role in blockwise analysis of motif. When user provide gene ID or gene name, transcription start site retrieved from dbTSS will be considered as reference point. And when user upload or paste the sequences, default reference point is the 'Start position' of the sequence which could be altered as per user's requirement.
Following is a pictorial representation, where source sequences are aligned with respect to their reference point. Black lines are the sequences. Reference point is denoted with reb block and yellow lines delimits the blocks of the sequences.
Choose Strand: User can select if he wants to analyze motif on only one strand or both the strand. Result for both the positive and negative strand will be given separately.
Threshold frequency: Threshold is defined as minimum no. of source sequences (represented in the form of percentage), in which given motif is expected to be present. Default value of threshold is 40, which can be altered by user if required.
Block Size: To find the common variants and co-variants, sequence will be divided into smaller blocks of sequences. Size of such blocks (in units of base pairs) will be defined using block size. Hence with lower block size, common variants and co-variants will be detected with less mean deviation and vice versa. Default value of block size is 250 nucleotides.
By entering the appropriate inputs, user can carry out blockwise analysis of sequence for the motifs. All the results will be produced on web-browser. If user wants to import to result, then one has to defined 'Project Name' and 'Email ID'. This input will allow software to process the inputs and send result to the given email ID.